What is zero trust?
Zero trust (ZT) is a security model wherein nothing is trusted; all users must be authenticated at each log-in to ensure their legitimacy. Full zero trust should be employed across every part of the infrastructure, endpoints, and stacks for services that a company runs. Consider a standard website with databases—each individual server or service by default does not trust anyone or anything. To be trusted, you need to be completely verified and identifiable. Another element of zero trust involves least privileged access, which is only giving access on a need-to-know basis to reduce a user’s digital footprint.
This security model analyzes behavior-based information to determine whether a behavior should be allowed or not. Having access to a certain part of a machine should not result in automatic trust.
Zero trust does not only apply to users. There can be zero trust networks, devices, and even processes. Regarding networks, zero trust takes into consideration where a person is accessing it from. Is it a known location? Are they allowed to access the network?
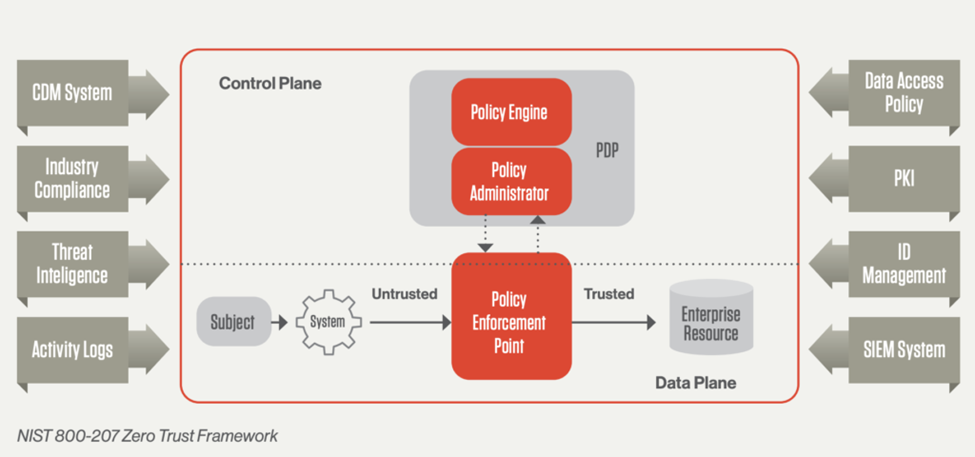
NIST SP 800-207
This is the National Institute of Standards and Technology’s (NIST) standard for zero trust and zero trust architecture. It defines zero trust as a model that moves security focus from the network to users, assets, and resources. Authentication and authorization are required at every stage and no implicit trust is granted.
Core principles
Continuous verification
Access should always be verified, at all times, for all resources. This can be executed through ways such as a strong password system and multi-factor authentication (MFA) along with a monitored permissions log. Here at Blue Team Alpha, if someone new receives elevated privileges, the security operations center (SOC) notifies us to verify whether this it is legitimate or if it is a threat actor elevating privileges on someone’s account.
Minimize impact
Having controls in place to slow down breaches or ransomware from spreading throughout the network.
Automate context collection and response
By maintaining behavioral data logs for every aspect of the IT stack you can notice anomalies and conduct in-depth investigations to verify what is and is not legitimate. By logging activities, you can stop users operating outside of their normal job responsibilities.
Logging all abnormal activity aids in identifying and stopping internal cyber threats and implements a system of checks and balances within your organization.
Implementation stages
Visualization
Understanding all the resources and their access points to visualize the associated risks. It is important to know what devices are running, where they are, and what is and is not allowed to be contacted.
Mitigation
Detect and stop threats to mitigate the impact of breaches.
Optimization
This is the hardest stage to complete. The goal of this is to extend protection to every part of the IT infrastructure; however, this can be a burden on productivity if the hosts take too long at the start of the day or if general access takes too long.
Why implement zero trust?
Zero trust is preventative protocol to protect your business. There are several benefits to implementing with the most important being able to limit the potential impact of a breach. If your company restricts the scope and permissions of a user, then the size of the attack radius can be reduced significantly. This prevents an entire organization from going down and decreases financial and reputational loss. While implementing zero trust is a higher cost up front, it is less expensive than costs accrued during a breach.
Every company should at least have a degree of zero trust like MFA implemented. The depth of zero trust is industry dependent and should consider how productivity is affected. Often, full implementation can be too much for small businesses due to a lack of personnel, so it is important to keep it to a manageable level.
Ultimately, zero trust is a way to protect your business and your data. Companies without even the most basic elements are at a much higher risk for severe attack. Some of the worst incidents we have seen at Blue Team Alpha involved companies who did not have MFA. Zero trust should grow with your organization, and it’s crucial to implement the basics as soon as possible. Contact Blue Team Alpha – we can help.




